SDCM & MacAdam Ellipses
SDCM is an acronym which stands for Standard Deviation Colour Matching. SDCM has the same meaning as a “MacAdam ellipse”. A 1-step MacAdam ellipse defines a zone in the CIE 1931 2 deg (xy) colour space within which the human eye cannot discern colour difference.
Most LEDs are binned at the 4-7 step level, in other words you certainly can see colour differences in LEDs that are ostensibly the same colour.
Due to the variable nature of the colour produced by white light LEDs, a convenient metric for expressing the extent of the colour difference within a batch (or bin) or LEDs is the number of SDCM (MacAdam) ellipses steps in the CIE colour space that the LEDs fall into. If the chromaticity coordinates of a set of LEDs all fall within 1 SDCM (or a “1-step MacAdam ellipse”), most people would fail to see any difference in colour. If the colour variation is such that the variation in chromaticity extends to a zone that is twice as big (2 SDCM or a 2-step MacAdam ellipse), you will start to see some colour difference. A 2-step MacAdam ellipse is better than a 3-step zone, and so on
Due to the variable nature of the colour produced by white light LEDs, a convenient metric for expressing the extent of the colour difference within a batch (or bin) or LEDs is the number of SDCM (MacAdam) ellipses steps in the CIE colour space that the LEDs fall into. If the chromaticity coordinates of a set of LEDs all fall within 1 SDCM (or a “1-step MacAdam ellipse”), most people would fail to see any difference in colour. If the colour variation is such that the variation in chromaticity extends to a zone that is twice as big (2 SDCM or a 2-step MacAdam ellipse), you will start to see some colour difference. A 2-step MacAdam ellipse is better than a 3-step zone, and so on
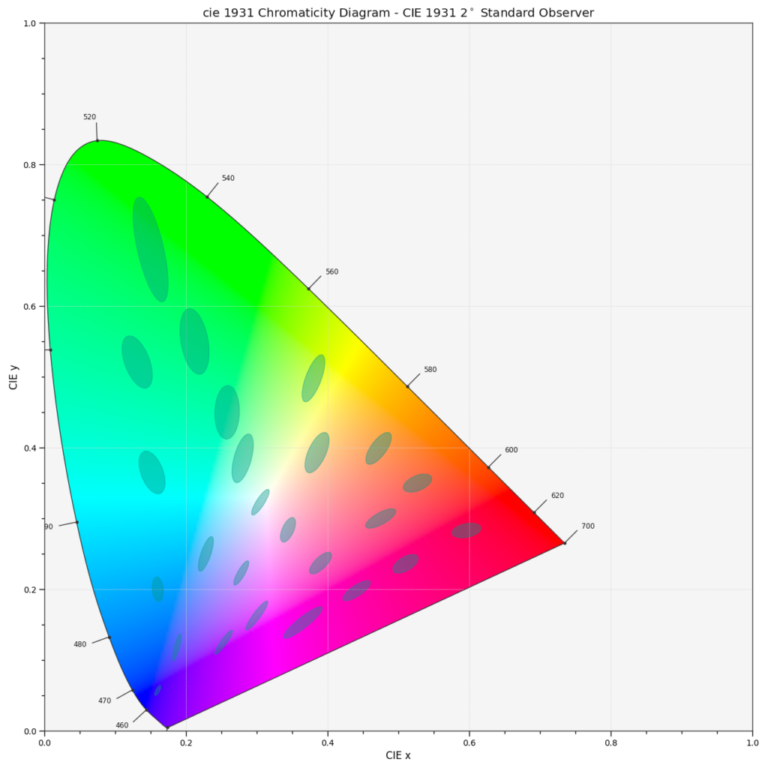
| MacAdam ellipses (SDCM) | Visibility |
|---|---|
| 1 SDCM | Almost no visible deviations |
| 2 SDCM | Deviations can be seen with instruments. |
| 3 SDCM | Few deviations visible with human eye |
| 4 SDCM | Visible deviations |
| 5 SDCM | Strongly visible deviations |
